Moulding Sand Testing

|
| (a) Moulding Sand Testing |
Are you looking for moulding sand testing methods used to test sand in a foundry?
This article discusses the 9 sand test types methods and equipment used in the foundry to test moulding sand with the proper formula, diagrams, summary, PPT and animation.
The list of moulding sand testing methods is as follows:
- Permeability test.
- Hardness test.
- Moisture content test.
- Clay content test.
- Grain fineness number (GFN).
- Green compression strength test.
- Green shear strength test.
- Dry compression strength test.
- Compatibility strength test.
A proper table of contents for the moulding sand testing method is given below for easy navigation for students. Students are advised to jump to any topic they want to learn.
{tocify} $title={Moulding Sand Testing Table of Content }
Permeability Test

|
| (b) Permeability test of moulding sand |
The permeability test is done by passing the quantity of pressurised air through the sand specimen under a given time and then putting those values in the permeability formula to gain the permeability number.
The permeability test is done to determine how much air passes through the sand specimen which will determine the permeability property of the sand.
Equipment for permeability test.
- Sand rammer (Used to make sand samples).
- Permeability measurement setup consists of a manometer (unitized to measure pressure) and specimen tube (for holding standard sand specimens).
Steps for taking permeability test.
Step 1: Green sand is rammed under the sand rammer to prepare the sand specimens. A 5cm x 5cm standard specimen of sand is used.
Step 2: The sand specimen is held by a tube called "sand specimen tube."
This standard specimen has Height =H in cm and Area = A in cm².
Step 3: Pressure (`P_{1}` in gm/cm²) at the start is measured.
Step 4: Air (Volume in `cm^{3}`) is passed through the sand specimen and pressure (`P_{2}` in gm/cm²) is measured at a certain time (T in seconds) at the end of the specimen.
Step 5: All the above values are put in the permeability formula to determine the permeability number.
Permeability number is defined as the volume of air that is passed through a specimen of 1 cm² in area, 1cm deep and pressure of 1g/cm².

|
| (c) Permeability test measurement |
As seen above in diagram (c) the pressure of air passed `P_{1}` is measured at the start of the specimen.
Air pressure `P_{2}` measured at the end of the specimen. `P_{1}` > `P_{2}`
Time is measured in minutes and height (H) is already defined.
These values are measured by and permeability number formula used to calculate the permeability number.
Permeability number formula (P) = `\frac{V*H}{p*A*T}`
V = volume of air `cm^{3}`.
H = Height of the sand specimen in cm.
p = Pressure of air `\frac{g}{cm^{2}}`
A= Cross-sectional area of the sand specimen in `cm^{2}`.
T= Time for the complete air to pass through the sand specimen in minutes.
Hardness Test

|
| (d) Hardness test of moulding sand |
A mould hardness test is performed in the foundry to determine the hardness of the mould after the ramming of sand is done.
The mould hardness test is important for the good hardness property of moulding sand.
The sand specimen used here is not green sand but dried and cured in the oven which does not have moisture in it.
Equipment for the mould hardness test.
- Hardness tester.
- Specimen tube used to make sand specimen.
Steps for taking moulding sand hardness test.
Step 1: Prepare the specimen in a specimen tube of desirable size
and shape.
Step 2: As this specimen still has moisture in it dry and cure it in the oven evaporating all moisture.
Step 3: Place the probe of the hardness tester on the dry sand specimen.
Step 4: Determine the hardness of the sand in the tester.
Why hardness test is done in the sand specimens?
Hardness indicates the resistance of the mould to plastic deformation and erosion of the sand when molten metal is poured into the mould.
The mould hardness is measured as BHN (Bittle Hardness Number) and is tested the same way we test the metal for hardness.
Moisture Content Test

|
| (f) Moisture content test of moulding sand. |
A moisture content test is done to determine the amount of moisture in the moulding sand.
A standard sample of the green sand mould of 50gm is used to measure moisture content in the sand.
Equipment for moisture content test.
- Infrared heater (Oven).
- Weighing scale (Utilized to measure the weight of the sample before and after moisture removal)
Steps for taking moisture content test.
Step 1: The moisture content test starts with weighing the sample. The standard piece can be around 50 gm. Let's call this sample weight `W_{1}`
Step 2: Once the green sand mould sample weight is measured sample is put in the infrared heater.
The temperature of the oven is kept between 105℃ to 110℃.
The objective of this step is to evaporate all moisture content out of the mould.
Step 3: Once the moisture is out of the sand, that sand sample is measured again to see how much moisture is evaporated. Let's call this sample weight `W_{2}` now.
Step 4: The difference between the initial weight `W_{1}` of the sample and the weight of the sample after the moisture has evaporated `W_{2}` is the moisture of the sand sample in percentage (%).
The formula to determine the moisture content test is as follows:
Moisture content formula = `\frac{W_{1}-W_{2}}{W_{1}}\times100`
`W_{1}` = Initial sample weight before evaporating moisture.
`W_{2}` = Weight of the sample after moisture has been evaporated from the oven.
Moisture content is measured in percentage.
Machines used to measure moisture directly are as follows:
Moisture teller machine:
Moisture content test is also done by putting a moisture sand sample in the machine called a moisture teller which measures weight, evaporates moisture and gives us the final moisture content result.
An instant moist meter is a piece of equipment that determines the amount of moisture present in the mould instantly.
Moistmeter-
Moistmeter is a portable moisture-indicating machine.

|
| (g) Moistmeter measuring moisture. |
Moisture is measured by inserting an electric probe into the mould. As mould is wet electric current will flow and tell the moisture in the sand directly as shown above in diagram (g).
Rapid moisture teller-
The rapid moisture teller test starts with mixing calcium carbide with the sand.
When calcium carbide gets in contact with moisture in the sand acetylene gas is generated.
The process is done in a vessel that is now full of pressure generated by acetylene gas.
This pressure is measured by the pressure gauge indicating moisture content in the sand.
More pressure means more gas means high moisture in the sand.
Why moisture content test is important?
- High moisture content in sand increases by more than 5% gas defects such as pinholes and blow holes also increase.
- Less moisture content in the sand below 2% reduces the strength of the mould.
Clay Content Test

|
| (h) Clay content test of moulding sand |
A clay content test is done to determine the amount of clay in the sand mould sample.
There are two types of clay in a sand mould. Active clay and non-active clay.
Clay becomes non-active above 500℃ it loses all its binding properties but clay is physically present.
I have described both tests to measure active and non-active clay down below.
Let us start learning a test to determine non-active clay first.
Clay content test to determine non-active clay.
Equipment for non-active clay content test.
- Oven for drying clay.
- Sand stirrer. (Used for stirring sand).
- Sodium hydroxide.
- Weighing scale. (Utilized to measure the weight of sand)
- Distilled Water.
Steps for taking a non-active clay content test
Step 1: A sample of 50 gm moulding sand is taken and weighed. Let's call this weight of sand `W_{1}`.
Step 2: Agitate the distilled water with sand and sodium hydroxide.
Step 3: Allowed sample to remain in the water for 10 minutes and settle down.
Step 4: After 5min we see sand particles and clay separated from each other in the water as shown below in diagram (i).

|
| (i) Clay content separates from the sand |
Step 5: Sand that is settled down in the clay is dried in the oven evaporating any moisture as shown below in diagram (j) below.

|
| (j) Clay from moulding sand dried in the oven |
Step 6: Settled clay is now weighted to determine clay content as shown in diagram (k) below. Let us call this weight `W_{2}`.

|
| (k) Clay content measured |
Clay content test to determine active clay.
Equipment for active clay content.
- Methylene blue is a chemical compound and a chemical dye.
- Methylene blue apparatus.
- 50 ml tetrasodium pyro-phosphate solution.
Step for taking active clay content test.
Step 1: Calibrate the methylene apparatus. (Number of methylene blue required/ bentonite)
Step 2: Mix 50 ml tetrasodium pyro-phosphate solution via pipette with 5gm of active sand in a stainless steel container.
Step 3: Disperse the sand particles using ultrasonic equipment.
Step 4: Fill the vessel slowly with methylene blue and stir the vessel.
Step 5: Clay is dried in the oven by passing hot air over it.
Step 6: The weight of the clay is measured directly after drying them in the oven. Clay weight is directly measured on a weighing scale.
Step 7: Active clay reacts with methylene blue in the vessel till a blue-green halo mark appears.
Step 8: After the mark has appeared we will stop the methylene blue supply and calculate the amount of blue methylene consumed and determine the clay content of the sand.
Step 9: Methylene blue only reacts with active clay and never with sand or dead clay. Calculate and determine the clay content in the sand.
Why does determining clay content tests become important?
- Excess clay reduces permeability increasing gas defects in casting.
- Very low clay content makes mould weaker.
Grain Finest Test

|
| (l) Grain fineness test of moulding sand |
GFN test is used to determine how fine to large size of sand grains are in total in the sand.
Equipment for GFN test.
- Sieve of different sizes.
- If done automatically a sieve shaker.
Steps for taking GFN test.
Step 1: Collect the sand to be tested and pour it into a sieve shaker.
Step 2: Vibrate the sieve shaker.
Step 3: This sieve has different meshes in it.
The sieve needs to be vibrated and a sieve with different meshes needs to be used to determine GFN.
The sieve on the top is a sieve with less meshed traps coarse grains.
The sieve at the bottom traps fine grains with high GFN.
Step 4: Stop the sieve shaker and remove all sieves.
Step 5: Determine the % of sand on every sieve.
GFN is large we have fine sand and if GFN is small that means we have course large size sand.
The formula for GFN is as follows:
GFN= Sum of the products/Sum of the % weights of sand retained.
GFN = `\frac{\sum_a^bM_{i}*f_{i}}{\sum_a^bf_{i}}`
`M_{i}` = Multiplying factor of `i_{th}` sieve.
`f_{i}` = amount of sand retained on the `i_{th}`
GFN indicates size from fine, average size to large size.
Why does determining GFN become important?
Determining size and shape is important as this will determine the outcome and defects in the final sand casting.
Fine sand gives a better surface finish but casting will have gas defects because of less permeability.
While course sand grain size gives a rough surface finish casting will have a low gas defect.
So it is important that sand with mixed shapes and sizes is to be used to give a controlled result.
Compatibility Test

|
| (m) Compatibility test of moulding sand |
A compatibility test is done to indicate how much sand is able to compact and reduce in height when we ram the loose sand.
Compatibility indicates water tempering degree of green sand mould.
It is the percentage (%) of decrease in the height of a loose mass of sand under controlled compaction.
This test is important to determine the compatibility property of moulding sand.
Equipment For Compatibility Test
- Sand rammer.
- Scale attached to sand compacter to measure the reduction in height of sand.
Steps For Taking Compatibility Test
Step 1: Fill the specimen tube with sand.
Step 2: Strickle the sand and make it to the same level.
Step 3: Remove the specimen from the specimen tube.
Step 4: Place the tube under the sand rammer.
Step 5: Compact the sand specimen with a rammer.
Step 6: A reduction in height (h) will be observed in the sand specimen.
Step 7: Note and observe the reduction in compatibility in percentage (%) in the diagram (n) below.

|
| (n) Compatibility test of moulding sand measurement |
Why compatibility test is done?
During ramming, the operation mould is compacted to get desirable compactness for the mould.
If sand mould is too compact, mould will not release gasses out of the mould giving gas defects.
If sand mould is loosely compact mould can be weak and give rise to drop defects.
During the sand casting process, molten metal is poured into the mould it is expected that the mould will remain intact and at the same time allow all gases to escape.
For the above reason, a compatibility test is done.
Green Compression Strength

|
| (o) Green compression strength of moulding sand |
Green compression strength is measured using a universal sand strength machine that is used to determine the compression of green sand under compressive force.
This test is important for determining the green strength of moulding property sand.
Equipment for green compression strength test.
- Specimen tube.
- Universal sand strength machine
- Sand rammer.
Steps For Taking Green Compression Strength
Step 1: Fill the specimen tube with sand.
Step 2: Place the specimen under the sand rammer.
Step 3: Allow the specimen to go through compressive force in the ram and remove the specimen from the rammer.
Step 4: Place the compressed specimen on a universal sand strength machine to measure green compression strength by passing the specimen through compressive forces as shown below in the animated diagram (p).
The universal sand strength machine breaks the specimen and indicates the compression strength on the indicator.
The unit for measuring green compression strength is Mpa or `\frac{N}{mm^{2}}`.

|
| (p) Green compression strength of moulding sand measurement. |
Why green compression strength test of moulding sand is done.
A green compression strength test is done to check the strength of mould under the compressive forces when mould is freshly made with a mixture of sand and moisture assuming actual mould going through compressive forces during sand casting.
This sample specimen of sand is not cured and has moisture in it.
Green Shear Strength

|
| (q) Green shear strength of moulding sand |
Green shear strength is used to measure the strength of the moulding assuming a real-life situation where a pattern is taken out from the mould.
Equipment For The Green Shear Strength Test
- Specimen tube for producing standard green sand specimen.
- Sand rammer for ramming specimen.
- Universal sand strength machine for testing strength.
Steps For Taking The Green Compression Strength Test
Step 1: Fill the specimen tube with wet sand and make a sand specimen for the shearing operation.
Step 2: Remove the specimen which is in the form of pads with projection.
Step 3: Allow the specimen to go through shear force by placing the specimen under a universal sand strength machine to measure shear strength as shown in animated diagram (r) below.
Step 4: Universal sand strength machine breaks the specimen and shear strength is indicated on the machine indicator.
The unit for measuring green compression strength is Mpa or `\frac{N}{mm^{2}}`.

|
| (r) Green shear strength of moulding under universal testing machine measurement |
Why green shear strength test of moulding sand is done?
When mould is freshly made mould is new and has moisture in it. This kind of mould is called green sand mould.
This test is done to test mould strength when removing the pattern from the mould. Mould should not shear in a real-life situation.
This test is done with freshly made green sand mould without mould being cured or dried.
Dry Compression Strength

|
| (s) Dry compression strength of moulding sand |
Dry compression strength is measured using a universal sand strength machine by subjecting a sand specimen to compressive loading.
This test is done to determine the dry strength property of moulding sand.
Dry Compression Strength Test Equipment
- Specimen tube.
- Universal sand strength machine
- Sand rammer.
Steps For Taking Dry Compression Strength Test
Step 1: Fill the specimen tube with sand and ram it producing a standard-size sample.
Step 2: Use the oven to dry the sand and make it a dry specimen.
Step 3: Remove the specimen from the oven and place it on the universal strength machine as shown in the animated diagram (t) below.
Step 4: Measure the dry compression strength when the specimen breaks and determine the dry compression strength on the indicator of the machine.
The unit for measuring dry compression strength is Mpa or `\frac{N}{mm^{2}}`.
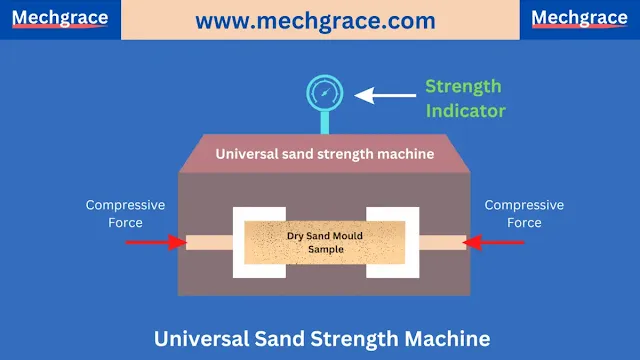
|
| (t) Dry compression strength of moulding sand measurement |
Why dry compression strength is done?
When high-temperature molten metal is poured into a mould entire moisture is evaporated and the mould is expected to withstand the shape under compressive forces.
A dry compression test checks the strength of the mould at this point.
Moulding Sand Testing Conclusion
The testing method used on moulding sand is the permeability test, hardness test, moisture content test, clay content test, grain fineness number (GFN), green compression strength test, green shear strength test, dry compression strength test and compatibility strength test.
Testing methods and types of equipment have been improving with time giving quick results and saving time in the foundry.
Mould sand testing is an important step in a foundry to get good sand casting without any defects.
Sand testing of moulding sand is important to determine moisture, permeability, hardness, various types of strengths, clay content and GFN of moulding sand which overall impacts how the final casting is cast.

