Types of Moulding Sand Introduction

|
| Types of Moulding Sand |
There are 8 types of moulding sand used in the sand moulding process that I have explained below.
This article discusses moulding sand types with diagrams, a summary, the difference between sand types, a moulding sand-related article section and PPT.
- Facing sand
- Backing sand
- System sand
- Core sand
- Green sand
- Dry sand
- Parting sand
- Loam sand
Facing Sand

|
| (a) Facing Sand |
What is facing sand in casting?
Facing sand is the first sand present in the mould cavity that comes in contact with molten metal.
This sand has carbon particles in it when burned forming a layer of gas preventing molten metal from penetrating the mould resulting in good surface finish casting.
Facing sand is shown below in animated diagram (b) with notation (1).
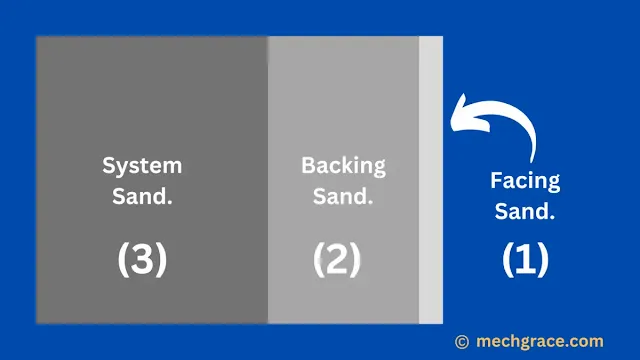
|
| (b) Facing Sand Animation |
Facing sand used in the foundry is sprinkled on the pattern first before we start making mould. This sand is called facing sand because sand is at the face of the mould and appears to be a thin layer.
Facing sand is fine having high GFN made up of sandstones.
Facing sand composition consists of fine sand, carbon, silica, clay and moisture.
What properties facing sand should have?
Facing sand used in a foundry should have the following properties to manufacture sand casting.
- High refractoriness.
- High strength and flowability.
- Hot strength.
Facing Sand Advanatges
- Reduction of metal penetration in the sand, sand always has some gaps between it this type of sand prevents metal from entering the mould by creating a barrier.
- An improvement over the surface finish and shine in the final casting.
- Reduction in surface defect of casting.
- Reduction in surface roughness.
Backing Sand

|
| (c) Backing Sand |
What is backing moulding sand in casting?
Backing sand is freshly prepared sand that follows facing sand and is black in colour.
Backing sand is also called black sand that backs the facing sand.
This sand is poured after facing sand to make the mould.
Shown below backing sand animation diagram (d) with notation (2) in between facing sand and system sand.

|
| (d) Backing Sand Animation |
Backing sand has clay, moisture and silica in it bonding together to form strong mould.
Backing sand has a combination of fine and medium size sand grains.
What properties backing sand should have?
Backing sand used in the foundry should have the following sand properties for sand casting.
- High permeability to let gasses pass out of the mould but at the same time maintaining compatibility property.
- Cohesiveness or strength property, failure of this property will cause defects.
- Green strength when sand is wet, dry strength when moisture evaporates and hot strength when molten metal is poured into the mould.
Moulding or backing sand does not have any used sand in it but this sand should have usability properties so it can be reused as system sand in the next mould.
System Sand

|
| (e) System Sand |
What is system sand in casting?
System sand is used sand that follows moulding or backing sand.
System sand forms the majority of sand in the mould.
Shown below is the system sand animation diagram (f) with notation (3).
This sand is poured at the last in the flask filling the flask fully.

|
| (f) System Sand Animation |
System sand is used sand (sand from previous sand casting mould) which is reactivated with water and binder agents.
System sand used in the foundry has a combination of medium to large coarse grain sizes.
What properties should system sand have?
The properties that system sand should have for the sand-casting process are as follows:
- Conductivity to remove all heat from the mould.
- Strength property and permeability.
- Adhesiveness property to stick to the flask while mould making.
- Collapsibility while removing the casting.
Core Sand

|
| (g) Core Sand |
What is core sand in casting?
Sand used for making core is called core sand.
Core moulding sand consists of sand, water (3% to 6%), core oil (1%), binders and additives.
Organic binders give more strength to the core sand.
Core oil used is made up of resin, linseed oil and molasses.
Other additives elements such as flour, wood flour, iron oxide and pitch are added to the core sand.
Baking the core sand gives better core sand properties to the core.
Coarse sand is used for the core to produce steel casting while fine sand is used for non-ferrous casting.
I have written a detailed article on the material used in the core including core sand and binders. I have discussed core sand and other materials in core material article.
What properties should core moulding sand have?
Core sand should have the following sand properties.
- Coolaspsibility. (Core sand should be able to collapse)
- Friability. (After the casting is done core sand should have the property to crumble)
- Refractoriness so core sand should sustain high-temperature molten metal and permeability to let gases escape from the core sand.
Green Sand

|
| (h) Green Sand |
What is green sand?
Green moulding sand is freshly prepared sand that has more than 5% water content and up to 30% clay.
It is called green sand not because of its colour but because of the moisture in it.
Water or moisture in sand activates the clay binding sand grains together and retaining its shape under pressure. Moulds made from these sands need to be compacted under a ramming machine to increase their compacting properties.
Coal dust is used extensively used with green sand to improve its surface finish quality and to prevent metal penetration of the metal in the skin surface of the mould.
Green sand finds application in the green sand moulding process. This sand is sometimes referred to as clay sand.
This sand needs to be used with additives such as sawdust, wood flour, husk, peat and cereals to increase the strength of the mould.
This sand is used for manufacturing green sand casting using green sand moulding process.
Green sand is taken directly from the river beds and further processed for sand casting.
Cores made from green sand have tendencies for hot tearing and developing internal stresses. Green sand is not capable of producing moulds for intricate castings.
Green sand has a disadvantage on the pattern, the pattern absorbs moisture in the green sand and there is an increase in the dimensions of the pattern resulting in uneven and enlaged casting.
Metal and plastic pattern material is best suited for this type of sand.
Taguchi techniques can be used along with green sand for making green sand moulding process.
Green sand is best for making green sand cores used to make cavities in green sand casting.
Green Sand Advantages
- The cost of green sand is low and is able to handle high-temperature metal.
- This sand has the highest hot strength and green strength property.
- Easily mouldable into moulds and best for ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
- Used for mass production of green sand moulds.
- The affordability of the sand is high for producing large moulds.
- Favourite sand for producing green sand moulds in the small-scale foundry industry.
- Can be used with higher moisture and clay content.
- Best for making moulds for small-size castings.
- Can be directly used in moulds after removing impurities. This sand does not need any further processing.
- This sand is available in circular, angular, coarse and fine structures for making variations of green sand and skin-dried moulds.
- This sand has high collapsibility properties and reusability properly.
- Favourite sand for home hobbyists for making small intricate backyard castings.
- Consumes less energy, and resources and improves profit for the foundry.
- Improves lead time delivery of casting after production of moulds is done with automation using machine moulding.
- Green sand mixed with dextrin gives a better casting result improving the hardness of the mould and other mechanical properties.
Dry Sand

|
| (i) Dry Sand |
What is dry sand?
The dry sand mould is formed when green sand is subjected to the heat in the oven at a high temperature evaporating all moisture from the sand.
Dry moulding sand finds its application in the dry sand moulding process for making a large-size casting.
Dry sand application is highest in the large foundries for producing dry sand casting in the dry sand moulding process.
All moisture from the sand evaporates making sand dry and hard retaining the initial shape.
Dry sand gives less pinhole, porosity and other gas defects as moisture is absent in the sand.
Dry sand is used for making dry sand casting products using dry moulding process.
Patterns of all materials can be used for making dry sand moulds. Wood, plastic, metal, wax, thermoform and plaster of pairs have no impact on change in dimensions of the final pattern and casting due to moisture content in sand.
Cores used by making dry sand are called dry sand cores. These cores are made from dry sand, which means all moisture from the core is taken out improving its strength, hardness, stability and hot strength.
What is the difference between green sand and dry sand?
The difference between green sand and dry sand is explained below.
| Green sand | Dry sand |
|---|---|
| 1) Green sand has moisture in it. | 1) Moisture is evaporated and dried in the oven. |
| 2) Gives gas defects such as blowholes, porosity and pinholes. | 2) Does not give gas defects due to the absence of moisture content in the sand. |
| 3) Used for green sand moulding. | 3) Used for dry sand moulding. |
Dry Sand Advantages
- Able to handle high-temperature metal for large-size intricate sand casting.
- Reduction in moisture-related defect as compared to using green sand.
- Can be used using different kinds of binders such as sodium silicate and resin.
- Can be used to make the core have a better capacity to produce holes and recesses in the casting with a reduction in hot tearing defects.
- Can be used for moulding high temperature, ferrous metals, malleable iron, ductile iron, steel and cast iron metals.
- Dry sand does not increase the size of the wooden pattern making it best suitable for wooden material patterns.
Loam Sand

|
| (j) Loam Sand |
What is loam sand?
Loam sand has a paste-like texture having 50% clay content in it.
Sand, clay and water are mixed to give a thick paste of sand which is used to make loam sand moulding.
Loam sand is used to make the solid casting with large sizes without using a pattern.
Loam sand is used in loam sand moulding for making bell shape casting using a sweep pattern.
Parting Sand

|
| (k) Parting Sand |
What is parting sand?
Parting sand is used to avoid sand sticking to the pattern and is also used between cope and drag in split mould.
Parting sand is sprinkled on the following board first while making the mould for sand casting.
This sand is free from the clay and is dusted to avoid cope, drag and pattern clinging to each other.
As shown below in an animated diagram (l) with an arrow parting sand separating cope and drag.

|
|
(l) Parting Sand Animation |
Parting sand apart from separating cope, drag and pattern does not serve any functional purpose in the mould cavity for making casting as it is always outside the mould cavity and does not come in contact with molten metal.
Final Conclusion
There are 8 types of sand in moulding which include facing sand, system sand, core sand, backing sand, parting sand, loam sand, dry sand and green sand.
The sand used in moulding should have specific properties such as permeability, refractoriness, cohesiveness, adhesiveness, mould hardness, green strength, dry strength, hot strength, collapsibility and more in the list.
I have explained all the properties that moulding sand should have in properties of moulding sand article. Students are advised to go through that article to understand the moulding sand concept in detail.
These moulding sand go through moulding sand testing to determine a few properties that I have mentioned above.
Moulding Sand In Casting Related Articles
| Properties of Moulding Sand | Moulding Sand Testing |
