Core In Sand Casting Process Introduction
 |
| Core In Sand Casting |
What is basic one must know before learning core in the casting process?
Core is used in the casting process to make holes, undercut and cavities that cannot be produced directly in the casting process. Depending upon the size, shape, molten metal, design and type of final cavity core type are selected.
Cores are made in the foundry using a core box. Simple shape cores can be made from green sand to produce cavities that do not have high accuracy requirements at a lower cost.
Moisture-free dry sand is used to produce a dry sand core. Apart from using green sand and dry sand, synthetic sand is used for producing highly accurate cores for complex cavities.
Sand cores made in this process are an important and crucial step for producing final sound casting with the required holes in the sand casting process.
As technology advances 3D-printed cores are used in the casting process. In the following article, I have discussed the function of the core, what supports the core in mould, advantages of the core, core types, core design and application.
{tocify} $title={Core In Sand Casting Process Table of Content }
Core In Casting Process
What are cores in the casting process and the function of the core?
A sand core is a tool made of refractory material used to make internal cavities, projections, undercuts, holes and geometry in the final casting.
Cores are made up of sand used for making the hole, recess, and hollow interior throughout the casting.
A core is a disposal object placed in the mould cavity to form internal cavities in the final casting as shown below in diagram (a).
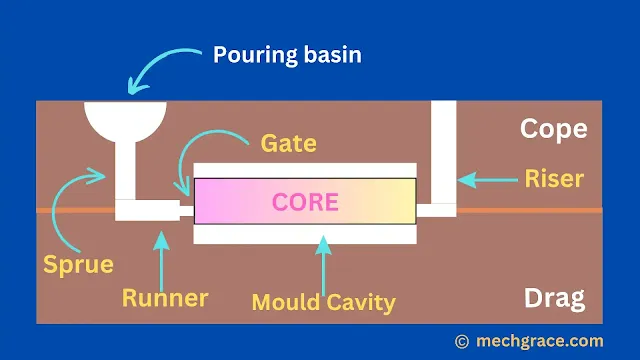 |
| (a) Core In Mould Cavity During Sand Casting |
Molten metal passes through the pouring basin, sprue and reaches in the mould cavity through the gate filling the mould cavity.
After molten metal fills the mould cavity, molten metal surrounds the core to make a hollow casting as shown in diagram (a) above.
Sand cores are used in the casting process when it is not practically possible to make holes throughout the pattern only.
Cores are supported by a metallic chaplet in the mould cavity.
Cores remain in the moulding sand from the pouring operation to the solidification of casting. After the casting is solidified casting is taken out along with cores.Cores must be stronger than mould with good hardness and should be able to handle the shrinkage of molten metal during solidification.
These cores are destroyed after the casting has been taken out.
It should be noted that cores should be only used where it is necessary. If it is possible to create the cavity in the casting product through machining cores should be eliminated.
Having cores in the casting process is a complicated method for producing holes and recesses in casting.
What supports the core in mould?
Chaplets and core print support the core in the mould. A core is supported by chaplet from the pouring operation to the solidification of casting.
I have written a separate article on chaplets in sand casting discussing types of chaplets and functions with diagrams that students are advised to read.
What is core box in the casting process?
Core boxes are boxes made from wood and metal to give shape and size to the core. Sand is prepared and rammed in the core box to make a core.
That is why I have written a detailed article about core box in casting with diagrams.
Engineers should go through this article to understand core boxes and the types of core boxes in the casting process.
How many types of cores are there?
Sand core in the casting process can be classified into different ways depending upon the type of material used for making the core and the position of the core in the mould cavity.
Depending on the sand, moisture, resin other materials used, sand cores are classified into three types.
- Dry sand cores in sand casting.
- Green sand core in sand casting.
- Shell cores are made from a mixture of sand and resin to make complex shape cavities.
Furthermore, cores can be classified into 9 types depending on the position of the core in the mould cavity.
That is why I have written a detailed article on the types of cores in sand casting with detailed explanations and diagrams.
What is core print in casting?
Core prints in the casting process support the core in the mould cavity.
Core print is an extension of core, I have written a detailed article on core print in casting with the difference between core print in casting and chaplet.
How are cores made in sand casting?
Cores are made in the casting process similar to how sand moulds are made with some differences. Cores are made in the sandbox.
Core boxes are used here to give shape and size to the core.
A core is of two types dry core and sand core.
I have written a detailed article here about the core making process in sand casting from the preparation of the sand mixture to the finishing of the dry core after the core has been cured.
What materials are used for making core?
Sand, binders, coating or core wash are used to make the core. I have listed materials used for making core in core material in casting article.
What are the characteristics and requirements for core in casting?
For selecting a core for a particular sand casting it is important to think of the requirement of the core material for the successful creation of a hole or recess in the casting.
The characteristics of the core have been discussed in detail.
The foundry engineers must note this in the sand casting process.
What forces act on the core in the mould cavity during the pouring of molten metal?
When molten metal is poured in the mould cavity during the sand-casting process molten metal tends to uplift the core due to buoyancy forces.
Buoyancy forces acting on the core are calculated by the following formula.
`P=V(\rho-d)`
`\rho`= Weight density of the liquid metal `\frac{N}{cm^{3}}`
P = Buoyancy force in N
V= Volume of core in `cm^{3}`
d= weight density of core material in `\frac{N}{cm^{3}}`
Core Design
What care must one take while designing the core?
- Parting Line Of Core- The design of the core must be as simple as possible. The core must be designed from an economical and manufacturing point of view. Parting lines on the core must be simple and not be irregularly increasing the cost of production.
- Necessary For Secondary Operation- Green sand cores must be used where there is a need for machining operation irrespective of the type of surface finish that is to be obtained after the casting.
- Core Support- Cores should have good support so they do not move when molten metal enters the mould cavity at a higher velocity.
- Multiple Cores- When using multiple cores, care must be taken if they have the same parting line.
- Proper Ventilation- Cores and coreprints must have proper ventilation allowing gases to escape from the cores and reducing gas defects in the cavity. Vent holes, fins and cleanout holes should be given for smooth exit of gases, water vapour and steam from the core.
- Sharp Corners- Sharp corners must be avoided reducing the erosion of the green sand cores. Corners should allow molten metal to pass through it smoothly.
- Length Of Core- The core should not be too lengthy that it will sag creating an uneven hole in the sand casting also these kinds of cores require more supporting structure.
- Simple Design- The core should be simple in design and easy to produce reducing the production cost of the core making in the foundry.
- Uniform Structure- Cores should be produced in such a way that the cooling of the casting around the core should be uniform to reduce the hot tears near the cores. Sudden uniform changes in sections of the core will give hot tear defects in the cavities, holes and sections of the casting.
Advantage Of Core In Casting
What are the benefits/merits of using core in the casting process?
The advantages of using a core in sand casting are as follows.
- Quality Cavities- High-quality casting with internal features and hollow sections can be produced using a dry core.
- Complex Cavities- Cuts, impressions, holes and pockets that cannot be achieved using pattern only are cast using cores. Complex internal cavities, shapes and tapered geometry can be created.
- Molten Metal Flow Control- The flow of molten metal in the mould cavity can be easily controlled using a core.
- Molten metal and core- The Core can serve as a directional element in sand mould when molten metal flows around the core. Molten metal can be directed using a core to fill the mould cavity and sections of the cavity completely.
- Core Simulation- Advanced modelling and simulation techniques are used to produce precise cores in the foundry. Core simulation software predicts how the core is going to function in the mould from pouring operation to solidification operation. This helps designers produce accurate cores.
- Collapsable Core- The core can be designed with special features for core collapsing and easy removal of cores.
Application of Cores In Casting
- Core finds its application in making cavities in engines for cylinders.
- Centrifugal pump housing.
- Spur gear cavity in the centre to place shaft.
- Pump housing.
- Electric motor housing.
- Circular bushes.
