Core Making In Casting Process
 | |
|
How are cores made in the sand-casting process?
Cores are made in a foundry so sand casting can be produced with holes and recesses.
Cores are manufactured in a foundry in two ways.
- Conventional method.
- Automatic hot core box method.
The step-by-step process used for making sand core in the casting process is as follows:
- Preparing core sand.
- Core moulding using a core box.
- Baking core in an electric furnace.
- Core removal from the mould.
- Core finishing.
Core Making Steps In Casting
Step 1 - Sand Preparation For Core
 |
| (a) Sand and Binding Mixture In Core Making Process |
Mixing of the ingredients is done first. Muller and core rollers are used to mix sand and binding agents such as clay together.
Commonly used organic binders used for core making are as follows:
- Vegetable oil.
- Core oil.
- Linseed oil.
- Corn oil.
- Resin.
- Sulphite.
- Sodium silicate.
- Molasses.
- Dextrin.
- Cereals.
- Coal tar.
- Petroleum oil.
Sand and binding agents are mixed until a uniform homogeneous mixture is formed.
Core roller mills are best for mixing core sand, and binding agents such as cereals as shown above in diagram (a).
For binders such as clay mullers mixers such as muller is used.
Step 2 - Core Moulding
Packing of the core sand is done in core boxes.
Cores are made with the help of core boxes.
Core boxes basically have cavities used to make cores of desirable shape and size.
Core box is of the exact shape and size of the core to be produced.
Core sand mixture prepared early is poured into the core box. Core sand is rammed manually or can be done on the core moulding machine.
Supporting reinforcement such as wires and rods are used to give core strength.
Wires made from carbon steel and cast iron wires are used to give support to the cores.
Sand core-making machines are of two types:
- Core blowing machine.
- Core ramming machine.
In the core blowing machine sand is blown and compressed using pressurised air.
In the core ramming machine core sand is poured into the core box and sand is compressed with plates.
Cores are vented to produce high-quality defect-free hole cavities.
Core sand must be compact enough to pass all gases during the sand-casting process.
There is not much difference between sand moulding of mould and cores.
The same principles and methods are applied to making core.
Core vents are added to the cores to allow gases to pass through the cores.
This avoids the formation of blowholes defects in sand casting.
If we want to make green sand core foundry engineers should stop over here and use green sand core directly in the moulding process or sand casting process.
Note: The following steps are only done to make the dry sand core.
Step 3 - Sand Core Baking
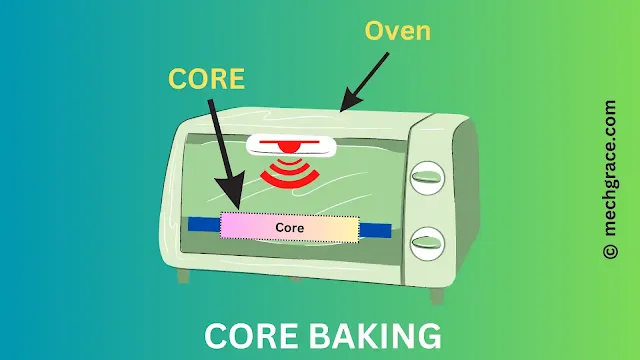 |
| (b) Core Baking |
Sand core baking is also called core curing.
Curing can be done in three ways and they are as follows:
- Cold box curing.
- Hot box curing.
- No-Bake curing.
In cold boxes curing gases are used to cure the core sand.
In the hot box curing sand core is heated up to 200℃ to 250℃.
In no-bake curing, binders are used to make the core. No heat and gases are used.
As shown above in diagram (b) core is being baked in the oven.
Core sand used for making core is mixed with a binding agent such as clay.
Moisture is used to activate clay in the core sand.
This clay needs to be cured along with sand removing all excess moisture from the sand core.
For this purpose core taken out from the core box is baked in the dielectric bakers and ovens.
Depending upon the duration of baking time and temperature core strength, moisture content and dryness within the core are decided. The core is baked from 200℃ to 400℃.
Hot air is passed on cores to dry the core and strengthen the binding agent.
Types of equipment used for core baking are as follows:
- Ovens.
- Dielectric Bakers.
Core baking is done in small batches using a batch conventional oven and for small to medium-type cores for continuous production ovens are used having conveyor belts.
Conventional ovens are heated using oil, coke, gas and coal.
Modern dielectric ovens use electricity to heat the heating elements to achieve close control over temperature with faster operations.
Ovens used for the continuous production of cores have a rack lined up with cores passing through hot air.
Cores are placed on conveyors and passed through hot air continuously it is important that cores have the same shape and size. Time and temperature during the process widely depend on the dimensions of the core.
Dielectric bakers have high-quality control over temperature for producing cores as heating elements such as plates and electrons are heated electrically.
Dielectric baking ovens are best for thermoplastic resin as binding agents.
Dielectric ovens have added advantages over conventional ovens with good control over temperature, faster heating function and a timer feature.
Large dry cores are assembled together using bolts and nuts.
Step - 4 Core Removal From The Mould
After the casting has solidified cores are to be removed from the mould.
Cores are designed to easily break and remove from the mould without damaging the casting.
The core is designed in such a way that the core should be easily removed from the mould. In order to do this core should have collapsable property.
Step - 5 Core Finishing
The core taken out of the electric oven does not have a good surface finish.
The core should have a good surface for producing hollow casting with holes.
The core taken out is trimmed and filled removing unwanted fins and rough surfaces.
Cores are trimmed using files, hard rubber, wires, emery stones and paper.
Grinding of dry cores is done on a grinding machine for a smooth surface finish cores.
When cores are used in sand casting care must be taken to avoid metal penetration in the core sand.
This is done by coating the core with a special coating liquid called core wash to avoid metal penetration in the core.
Normally cores are dripped in the coating fluid but the coating fluid can be sprayed and brushed.
This process of applying coating or core wash on the core is called core dressing.
For making large cores, cores are made from lead and bentonite.
For making small-size cores silica flour and graphite are used.
The coating core increases strength, reduces crumbliness and improves surface finish and appearance.
Core material used in the making process.
Core materials used with core washes are as follows:
- Mica.
- Graphite.
- Zirconium.
- Silica flour.
- Graphite.
- Silica with coal and coke.
- Flour
These core materials are mixed with a core wash to produce high-quality cores in a foundry.
I have written a separate article discussing core material in casting. Students are advised to read it for a better understanding of the core.
These core materials should have certain characteristics and properties to be selected as a core in the sand casting process.
