Types of Cores In Casting

|
| Types of Core In Casting |
Core is used for making hollow sections in the casting during the sand casting process in a foundry.
The core can be classified in two ways.
- Types of core based on sand.
- Types of the core according to the position of the core in a mould cavity.
Type of Core Based On Sand
- Green sand core.
- Dry sand core.
- Shell cores.
Green Sand Core
Green sand cores are made by a pattern by ramming the green sand around the pattern.
Green sand cores are weak and can only be used for manufacturing small and lightweight casting.
Green sand cores are a very economical and common type of core used for producing holes in casting.
These cores (pattern) cannot produce deeper holes and need a draft for the withdrawal of the pattern.
A green sand core is part of the mould only. Green sand cores have less strength and are more prone to causing moisture defects.
The process of making green core is the same as making green mould with the only difference being that the core is made in the core box.
Dry Sand Core
The dry sand core-making process consists of making the core in the core box and drying out the core in the oven.
The dry core-making process is explained in core making in sand casting article.
The advantage of using a dry-strength core is it has higher strength than a green sand core.
Dry sand core is free from moisture and reduces defects related to moisture as the dry sand core is dry.
Dry sand core at times serves as a bottom gate in the gating system.
Dry sand cores can be classified based on the type of curing process used to make dry cores.
- Cold box cured cores- Co2 gas is used to cure core sand using sodium silicate binder with silica sand.
- Hot box cured cores- Polyol-phenolic formaldehyde and poly-isocyanate binder is mixed with fresh silica sand and then passed through amine gas for 10-20 seconds to make a hardened core in the core box.
- No bake cure cores- Fine silica sand and urethane binders are mixed together to make a core to achieve a good surface finish and dimensional tolerance in the casting process.
- Shell cores- Silica sand and thermoplastic resin are mixed and heated in the metal box up to 230℃ to produce shell cores.
Shell Cores
Shell cores are made with a mixture of sand and resin.
This sand-resin mixture is cured in an oven to create complex shapes of cores with a thin wall.
Types of Core In Casting Based On Position of Core
There are 7 types of core in sand casting according to the position and state of the core in the mould cavity.
- Horizontal core.
- Vertical core.
- Hanging core.
- Cover core.
- Balanced core.
- Ram-up core.
- Wing core.
- Kiss core.
- Drop Core.
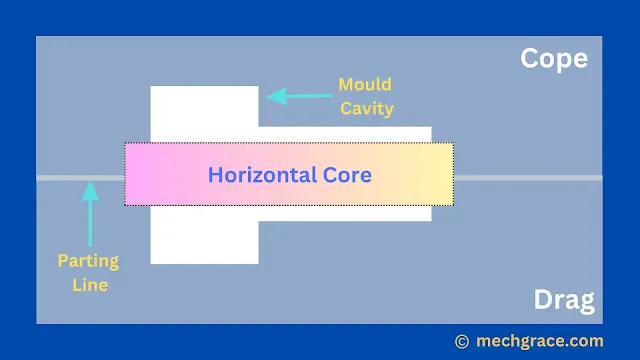
Horizontal Core
Horizontal core rests in mould along the parting line between cope and drag.
Horizontal cores are supported by core prints.
As shown below in diagram (a) horizontal core.
|
| (a) Horizontal Core |
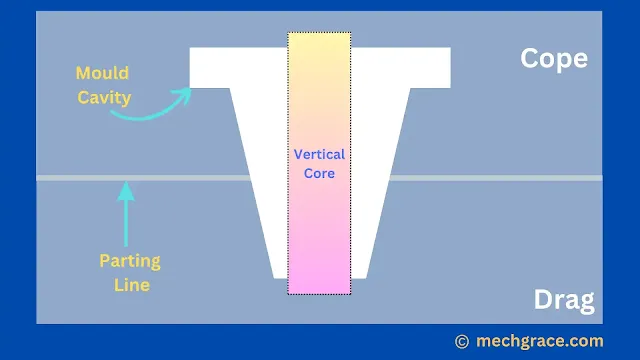
Vertical Core
Vertical core rest in cope and drag part of the mould.
Vertical cores have a high taper at the top and a small taper at the bottom of the core.
It is called a vertical core as it is placed and rested in a mould vertically.
As shown below in diagram (b) vertical core.
|
| (b) Vertical Core |
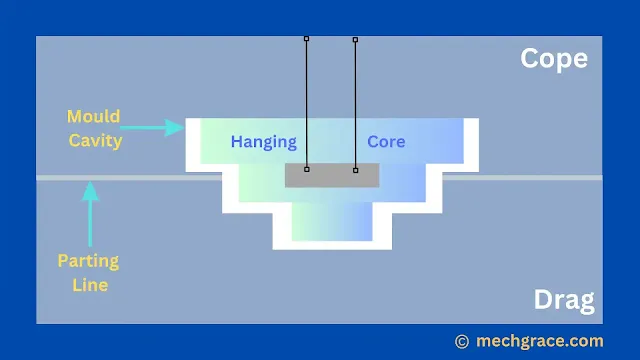
Hanging Core
A hanging core is called a hanging core because it hangs along the cope without any support in the drag side of the mould.
Hanging cores are supported by wire or rod.
As shown below in diagram (c) hanging core. A hanging core is called a hanging core because it looks and is hung with wires.
|
| (c) Hanging Core |
Cover Core
If cores are supported from the drag side of the mould only it is called the cover core.
The cover core has an opposite arrangement to the hanging core.
This is called the cover core as it looks like the core is covering the mould cavity.
As shown below in diagram (d) cover core.

|
| (d) Cover Core |
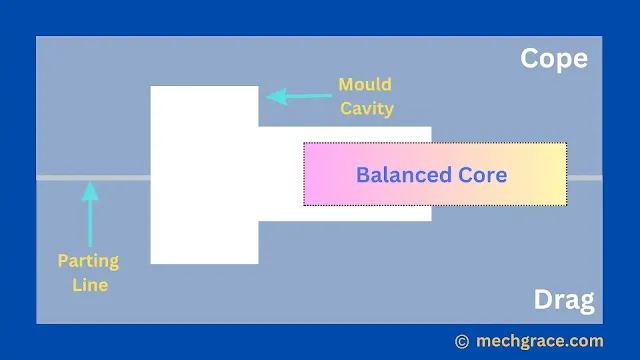
Balanced Core
A balanced core is a core in which only one side of the core is available for making holes in the casting.
While another side of the core is deep inside the moulding sand supporting the entire core.
A core is balanced by making the core longer and core prints support the core.
As shown below balanced core is in diagram (e) below.
|
| (e) Balanced Core |
Balanced cores are usually longer than other cores.
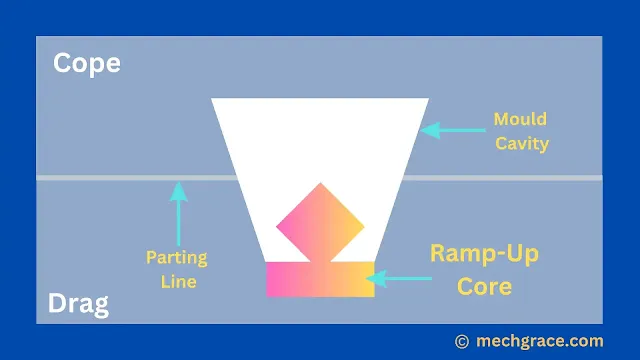
Ram-up Core
A ram-up core is set in the mould during the ramming of the sand.
A ram-up core is used when core details are in inaccessible positions so it becomes necessary to core impression during sand ramming.
As shown below in diagram (f) ram-up core is in the casting process.
|
| (f) Ram-up Core |
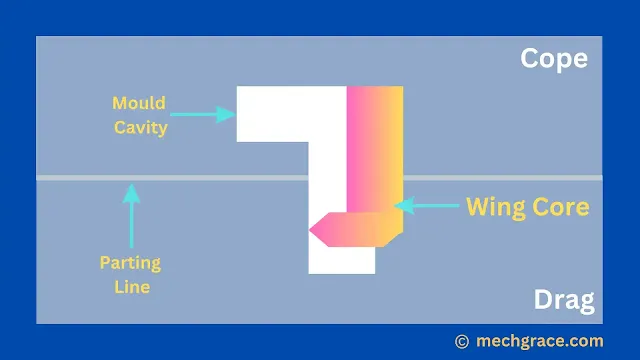
Wing Core
Wing core is used for creating recess above or below the parting line.
The core is given taper for easy accommodation of the core in the mould.
As shown below in diagram (g) wing core.
|
| (g) Wing Core |
Other names for wing core are drop core, chair core, tail core, and saddle core according to shape and position.
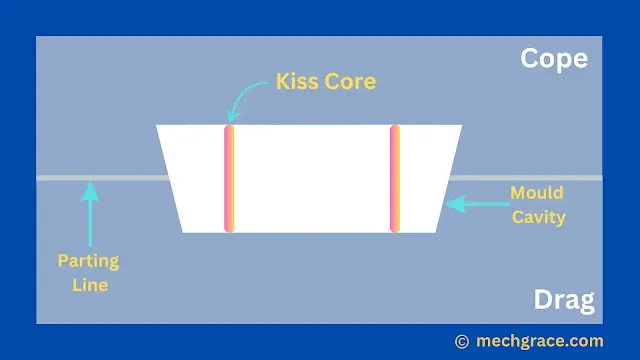
Kiss Core
Normally core is held in the mould with wires or core prints. But in the case of kiss core, no wires or core prints are used as supporting members for core placements.
A kiss core is simply held in the mould by the pressure of cope.
As shown below in the diagram of (h) kiss core.
|
| (h) Kiss Core |
Kiss core is used when the dimensional accuracy of the hole is not of primary importance.
Drop Core
The core used for producing cavities which are not in line with the parting surface is called a drop core. Drop cores are in the drag section of the mould.
